This article assumes you have a working IIS installation with SSL/TLS enabled and that you wish to add mandatory client certificate authentication. The scope of client authentication is such that the Certificate Request packet will reference 2 certificate authorities whose directly issued certificates can be provided to satisfy the server requirements. It is assumed that the implementation does not depend on AD users and only references local users, and hence "IIS Client Certificate Mapping authentication" as opposed to "Client Certificate Mapping authentication using Active Directory".
Download and install the certs in the correct stores
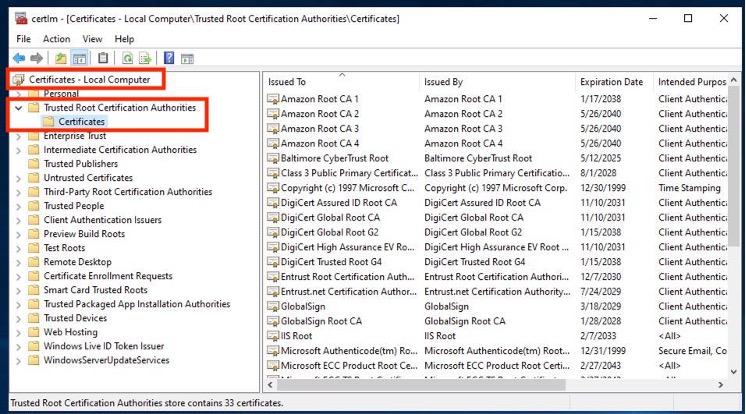
1. Install the NHS Root Authority and NHS Root Authority G2 CA certificates into the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for the Local Computer account
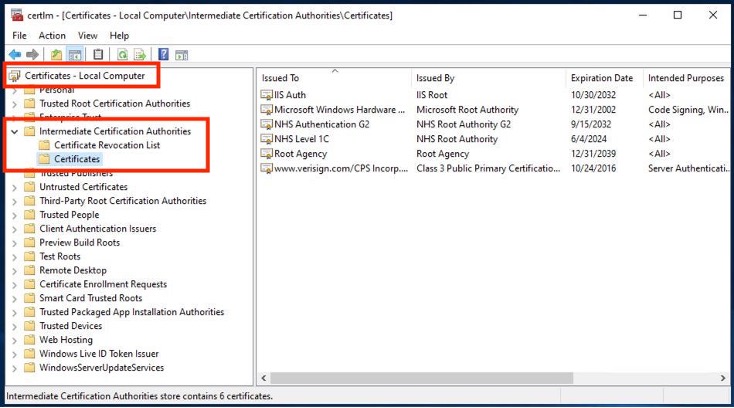
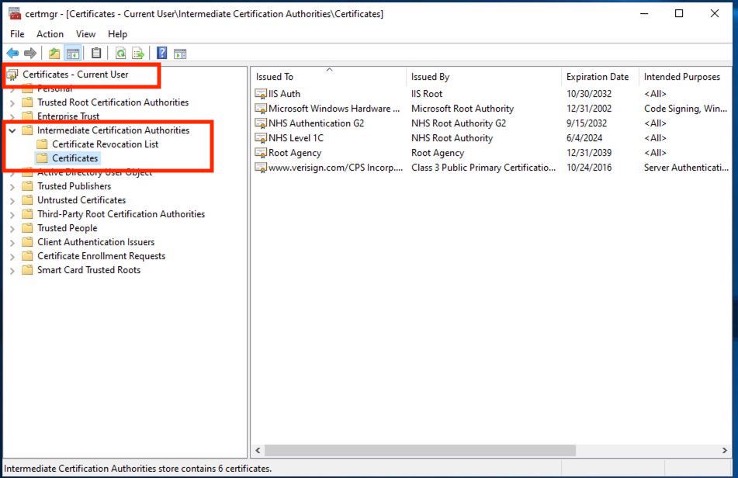
2. Install the NHS Level 1C and NHS Authentication G2 CA certificates into the Intermediate Certification Authorities store for the Local Computer AND Current User accounts.
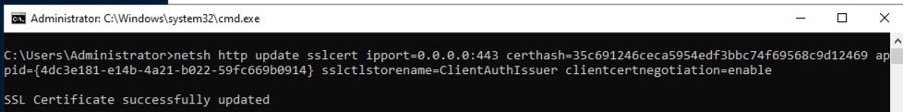
3. Run the following from a CMD prompt... netsh http show sslcert > %TEMP%\certs.txt
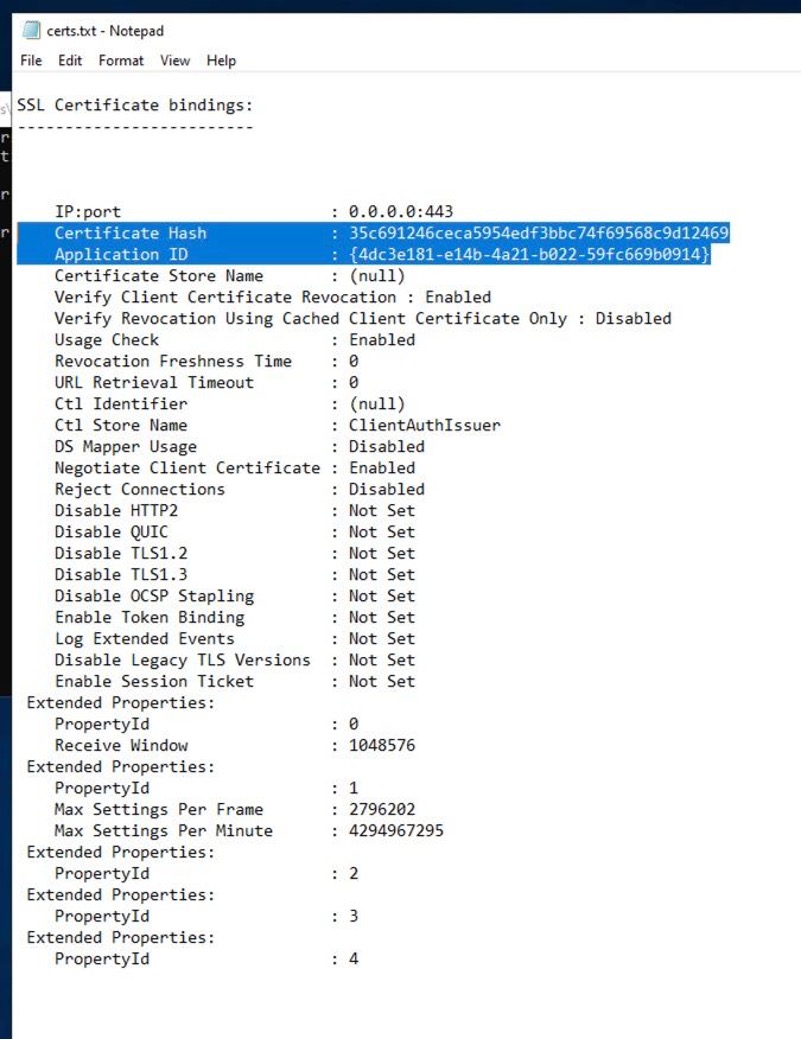
4. Open %TEMP%\certs.txt and locate the cert which matches the IIS binding for your website. It's likely the first in the list, bound to 0.0.0.0:443. Note the Certificate hash (eg. 35c691246ceca5954edf3bbc74f69568c9d12469) and Application ID values (eg. {4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914} - including braces)
4. Run the following command: netsh http update sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=CertificateHash appid=ApplicationID sslctlstorename=ClientAuthIssuer clientcertnegotiation=enable